Introduction
In the fast-paced world of modern manufacturing, industrial software has become the intelligent backbone of production systems.
Gone are the days when factories relied solely on machinery and manual control — today, software solutions manage, monitor, and optimize every stage of production, ensuring precision, safety, and efficiency.
From real-time data collection to process automation and predictive maintenance, industrial software empowers companies to achieve smarter, more connected operations across every production line.
What Is Industrial Software?
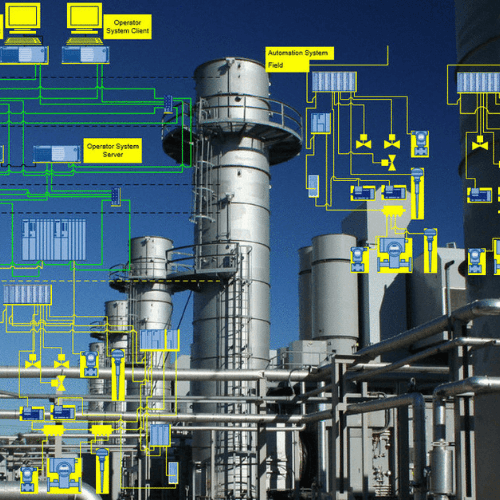
Industrial Software refers to specialized programs and control systems designed to monitor, manage, and automate industrial operations.
It serves as a bridge between hardware devices — such as sensors, actuators, and PLCs — and business management systems that rely on accurate data for decision-making.
Its main goal is to increase productivity, minimize human error, and ensure continuous operation with high precision and stability.
Main Types of Industrial Software
1. PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) Systems
The PLC is the heart of industrial automation.
It is a robust controller that processes inputs from sensors and executes commands to control machines or equipment on the production line.
PLCs are programmed using industrial languages like Ladder Logic or Structured Text, and they ensure continuous, real-time control in every factory environment.
Key Advantages:
-
Designed for 24/7 industrial operation.
-
Highly reliable and resistant to harsh environments.
-
Easy to program, modify, and maintain.
2. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) Systems
SCADA systems are essential for large-scale industrial monitoring and control.
They collect data from sensors and PLCs, visualize it in real-time, and allow operators to control the entire process from a single screen.
Core Features:
-
Real-time visualization of industrial processes.
-
Instant alerts in case of any fault or abnormal condition.
-
Historical data logging and performance analysis.
SCADA is widely used in industries like food processing, water treatment, energy, and packaging, where continuous monitoring is vital.
3. HMI (Human Machine Interface) Systems
The HMI is the interactive interface between the operator and the machine.
It provides real-time data display, status updates, and control options through touchscreens or control panels.
Key Benefits:
-
Intuitive and user-friendly interface.
-
Multilingual support (Arabic, English, Turkish, etc.).
-
Reduces human error and improves operational speed.
Modern HMIs are equipped with graphical dashboards that help operators monitor multiple processes at once, simplifying complex workflows.
4. MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems)
MES software acts as the bridge between shop floor operations and enterprise-level management systems (ERP).
It collects production data, tracks product movement, and provides real-time performance indicators to managers.
Benefits of MES:
-
Improves overall equipment efficiency (OEE).
-
Tracks production from raw materials to finished goods.
-
Reduces waste and enhances resource utilization.
The Role of Industrial Software in Industry 4.0
With the rise of Industry 4.0, industrial software has evolved from being a control tool to becoming the digital brain of smart factories.
It integrates with advanced technologies such as:
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) – for data-driven decision-making.
-
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) – connecting machines, systems, and people.
-
Cloud Computing – enabling remote monitoring and secure data access.
These integrations make factories smarter, predictive, and self-optimizing, capable of foreseeing faults and automatically improving performance in real-time.
Advantages of Implementing Industrial Software
-
Higher Operational Efficiency – Optimizes processes and minimizes downtime.
-
Enhanced Quality Control – Ensures consistency and compliance with standards.
-
Data-Driven Insights – Real-time data collection for faster decision-making.
-
Improved Safety – Automated alerts and control systems protect workers and machinery.
-
Scalability and Integration – Easily connects with future systems and upgrades.
Applications of Industrial Software
Industrial software is now an essential component in various sectors, including:
-
Food and Beverage Manufacturing
-
Pharmaceutical and Medical Production
-
Chemical and Detergent Plants
-
Packaging and Filling Lines
-
Automotive and Electronics Manufacturing
Conclusion
Industrial software is the foundation of digital transformation in manufacturing.
It enables machines not just to operate, but to think, communicate, and adapt to changing conditions.
With integrated control systems such as PLC, SCADA, HMI, and MES, modern factories are achieving higher levels of automation, safety, and performance — redefining the standards of industrial excellence worldwide.