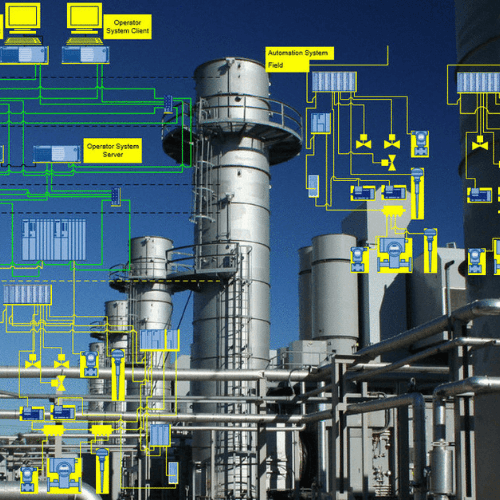
Introduction
Modern industries are undergoing a fundamental transformation driven by technological advancement and increasing market demands. Traditional manual operations are no longer sufficient to achieve the levels of speed, accuracy, and consistency required in today’s competitive manufacturing landscape. As a result, industrial automation has become a core element in the development of efficient, reliable, and scalable production systems.
Industrial automation is not simply about replacing manual work with machines; it represents a comprehensive operational approach that integrates equipment, control systems, and software to optimize industrial processes.
What Is Industrial Automation?
Industrial automation refers to the use of control systems, electronic devices, and industrial software to operate manufacturing processes with minimal human intervention. These systems are designed to monitor, control, and optimize production activities in real time.
The main objectives of industrial automation include:
-
Ensuring consistent and repeatable operations
-
Improving process accuracy and stability
-
Reducing operational variability
-
Enhancing overall production efficiency
Why Industrial Automation Is Essential Today
Manufacturers face increasing pressure to improve productivity while maintaining high quality and reducing costs. Industrial automation addresses these challenges by providing structured and controlled production environments.
Continuous and Stable Production
Automated systems are capable of operating continuously without fatigue, ensuring stable production output over extended periods.
Improved Process Control
Automation allows precise control of every stage of production, ensuring that processes are executed according to predefined parameters.
Reduction of Human Error
By minimizing manual intervention, automation significantly reduces the risk of errors that may affect product quality or production efficiency.
Core Components of Industrial Automation Systems
Control Systems
Control systems serve as the central intelligence of automated processes, executing programmed instructions and coordinating machine operations.
Measurement and Sensing Devices
Sensors and measuring instruments collect real-time data such as weight, speed, level, temperature, and pressure, providing critical input for process control.
Operator Interfaces
Human-machine interfaces allow operators to monitor system performance, visualize data, and manage operations efficiently.
Industrial Software
Software platforms process data, generate reports, support diagnostics, and enable performance optimization across production lines.
Impact of Industrial Automation on Product Quality
Product quality depends heavily on process consistency. Automated systems ensure:
-
Uniform operating conditions
-
Reduced variation between products
-
Accurate control of quantities and specifications
-
Lower rates of non-conforming products
Industrial Automation in Packaging and Production Lines
Packaging and production lines are among the most automation-dependent industrial applications. Automation in these areas delivers:
-
Higher production speeds
-
Accurate quantity and weight control
-
Reduced material waste
-
Improved consistency of final products
Automation and Workplace Safety
Industrial automation significantly enhances workplace safety by reducing human exposure to repetitive, heavy, or hazardous tasks. This contributes to safer working environments and improved operational reliability.
Cost Control Through Automation
Automation enables manufacturers to control operational costs more effectively by:
-
Optimizing raw material usage
-
Reducing unplanned downtime
-
Lowering maintenance costs through stable operation
-
Improving energy efficiency
Data-Driven Decision Making
Automated systems continuously generate operational data that can be analyzed to:
-
Monitor performance trends
-
Identify inefficiencies
-
Support predictive maintenance
-
Improve long-term production planning
Scalability and Long-Term Sustainability
Industrial automation provides flexibility that allows manufacturers to:
-
Expand production capacity with minimal disruption
-
Adapt to changing market requirements
-
Support sustainable manufacturing practices
-
Reduce waste and resource consumption
The Future of Industrial Automation
The future of industrial automation is focused on:
-
Greater system intelligence
-
Enhanced integration across production stages
-
Increased reliance on real-time data
-
Improved operational transparency and control
Automation will continue to play a critical role in helping manufacturers achieve long-term efficiency and competitiveness.
Conclusion
Industrial automation is a foundational element of modern manufacturing systems. By implementing well-designed automation solutions, manufacturers can achieve higher efficiency, improved product quality, reduced operational costs, and greater production stability.
Ultimately, industrial automation enables factories to operate smarter, faster, and more reliably in an increasingly demanding industrial world.