Introduction
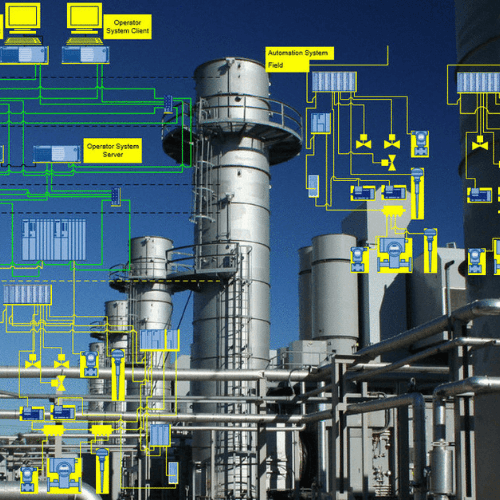
In the world of industrial automation, efficiency, reliability, and precision are essential. One of the most widely used technologies that empower smart factories is the Programmable Logic Controller (PLC). These systems are the backbone of automated production lines, ensuring smooth operations across industries in the Middle East, Gulf region, and worldwide.
This article explores what PLC systems are, how they work, their advantages, applications, and future trends shaping Industry 4.0.
What is a PLC System?
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is an industrial computer designed for automation. Unlike standard PCs, PLCs are built to survive harsh environments — from high temperatures and vibrations to dust and humidity.
They use special programming languages such as ladder logic, structured text, and function block diagrams to automate tasks, manage inputs and outputs, and control machinery in real time.
Main Components of a PLC System
-
Central Processing Unit (CPU): Executes the program and manages logic operations.
-
Memory: Stores operating programs and data.
-
Input Modules: Collect signals from sensors, switches, or meters.
-
Output Modules: Send control signals to motors, valves, and actuators.
-
Power Supply: Ensures stable energy for the system.
-
Programming Device: Laptop or handheld unit for uploading and testing programs.
Key Advantages of PLC Systems
-
Reliability in harsh conditions
-
Easy reprogramming for production changes
-
Reduced wiring complexity compared to relay systems
-
Real-time control and monitoring
-
Integration with SCADA, IoT, and MES systems
-
Troubleshooting and diagnostics for quick issue resolution
Industrial Applications of PLC Systems
PLCs are versatile and used across multiple industries in the Gulf and Arab region:
-
Manufacturing: Conveyor control, robotic assembly, process optimization.
-
Oil & Gas: Pump control, safety systems, pipeline monitoring.
-
Food & Beverage: Packaging, bottling, and automated quality checks.
-
Automotive: Welding, painting, and robotic production cells.
-
Water Treatment: Pumping, filtration, and chemical dosing.
-
Building Automation: HVAC systems, elevators, lighting control.
PLC Systems and Industry 4.0
With the rise of smart factories and digital transformation, PLCs are evolving to:
-
Connect with IoT devices for real-time analytics
-
Support AI-driven predictive maintenance
-
Enhance cybersecurity against industrial threats
-
Provide remote monitoring and cloud integration
This evolution makes PLCs not just controllers, but also data hubs for decision-making in modern industries.
Related Technology – Checkweigher Systems
Alongside PLCs, another vital automation solution is checkweigher systems used for real-time weighing and quality control in food, packaging, and pharmaceutical industries. For advanced checkweigher technology, visit ERS Checkweigher – a trusted provider of precision weighing and inspection systems.
Conclusion
PLC systems remain the core of industrial automation, offering flexibility, reliability, and efficiency for factories across the Middle East and globally. By integrating PLCs with modern technologies like IoT, SCADA, and AI, businesses can boost productivity, reduce downtime, and stay competitive in the era of Industry 4.0.
For companies looking to combine PLC automation with state-of-the-art quality inspection, solutions like ERS Checkweigher provide an added layer of efficiency and accuracy.