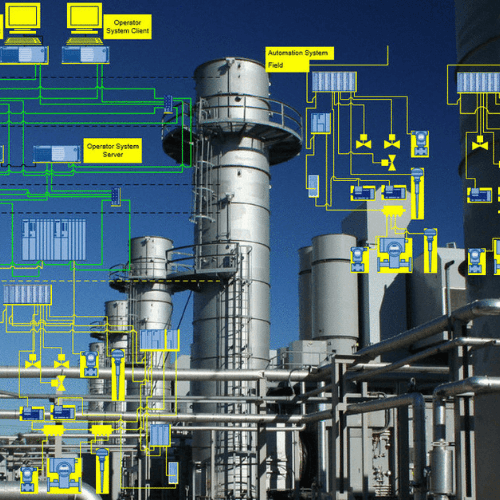
Introduction
Since the first industrial robot was introduced in the mid-20th century, Industrial Robots have revolutionized the way industries operate. Manufacturing shifted from manual labor to highly automated systems capable of working with precision, speed, and reliability.
Today, industrial robots are at the core of smart factories and play a crucial role in the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Industry 4.0). They enhance productivity, improve quality, reduce costs, and increase flexibility in production lines.
In this article, we will explore what industrial robots are, their main components, types, key applications, benefits, challenges, and the future of robotics in global industries, with a special focus on the Gulf region and the Arab world.
What Are Industrial Robots?
An industrial robot is a programmable mechanical machine designed to perform specific tasks in industrial environments, such as assembly, welding, painting, packaging, or material handling.
Key characteristics of industrial robots include:
-
High efficiency and repeatability.
-
Ability to work in hazardous or demanding conditions unsuitable for humans.
-
Flexibility to be adapted and reprogrammed for different tasks.
Components of an Industrial Robot
Industrial robots are composed of several interconnected parts:
-
Manipulator Arm
-
The core structure of the robot.
-
Made of joints and links allowing multi-directional movements.
-
-
Actuators
-
Drive the robot’s motion.
-
Can be electric, hydraulic, or pneumatic.
-
-
End Effectors
-
The “hands” or tools attached to the robot to perform tasks.
-
Examples: grippers, welding guns, painting nozzles, cutting tools.
-
-
Sensors
-
Enable the robot to perceive its environment.
-
Include force sensors, vision systems, heat sensors, and position sensors.
-
-
Controller
-
The “brain” of the robot.
-
Processes input from sensors and executes programmed instructions.
-
Types of Industrial Robots
Industrial robots come in different designs, each suited for specific applications:
-
Cartesian Robots
-
Move along three linear axes (X, Y, Z).
-
Ideal for assembly and material handling.
-
-
Cylindrical Robots
-
Operate along a cylindrical coordinate system.
-
Common in welding and assembly tasks.
-
-
Spherical Robots
-
Move within a spherical range.
-
Provide flexibility for wide-reaching tasks.
-
-
Articulated Robots
-
Feature multiple rotary joints resembling a human arm.
-
Widely used in automotive and heavy industries.
-
-
Delta Robots
-
Lightweight and extremely fast.
-
Common in packaging and food industries.
-
-
Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
-
Designed to work safely alongside humans.
-
Popular in modern smart factories.
-
Applications of Industrial Robots
Industrial robots are transforming a variety of industries:
-
Automotive
-
Welding, painting, assembly, and quality inspection.
-
-
Electronics
-
Assembling delicate electronic components.
-
Advanced quality testing.
-
-
Food & Beverage
-
Packaging, labeling, and palletizing.
-
Handling products in sterile environments.
-
-
Pharmaceuticals & Healthcare
-
Precise drug packaging.
-
Manufacturing medical devices.
-
-
Logistics & Warehousing
-
Parcel sorting and distribution.
-
Automated inventory management.
-
-
Construction
-
3D printing of buildings.
-
Heavy-duty tasks like drilling and material handling.
-
Benefits of Industrial Robots
-
Higher Productivity: 24/7 operation without fatigue.
-
Better Quality: Minimized human errors and improved consistency.
-
Reduced Costs: Lower labor needs for repetitive tasks.
-
Improved Safety: Keeps workers away from hazardous environments.
-
Flexibility: Can be reprogrammed for multiple tasks.
-
Global Competitiveness: Enhances efficiency and competitiveness.
Challenges of Industrial Robots
While beneficial, industrial robots also face certain challenges:
-
High Initial Costs: Investment in robots and infrastructure is significant.
-
Technical Expertise: Skilled engineers are required for programming and maintenance.
-
Workforce Impact: Potential reduction of certain human jobs.
-
Cybersecurity Risks: Especially as robots are connected to smart networks.
-
Downtime & Maintenance: Malfunctions can disrupt entire production lines.
The Future of Industrial Robots
With advancements in Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), the future of industrial robots is rapidly evolving:
-
Collaborative Robots (Cobots): More integration with human workers.
-
Smart Factories: Robots as part of interconnected, data-driven ecosystems.
-
Digital Twins: Virtual models to simulate and optimize robot performance.
-
Sustainable Manufacturing: Robots designed to reduce energy and resource consumption.
-
Expansion in the Gulf & Arab World: Driven by initiatives like Saudi Vision 2030 and investments in smart cities and advanced industries.
Conclusion
Industrial robots are no longer optional—they are essential components of modern manufacturing. They enhance productivity, reduce costs, ensure product quality, and improve workplace safety.
As we advance further into the era of Industry 4.0, industrial robots will continue to evolve and expand their role, becoming the backbone of global and regional industries, including those in the Gulf and Arab world.