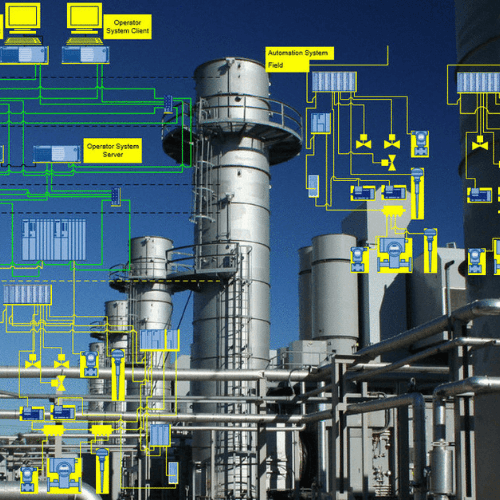
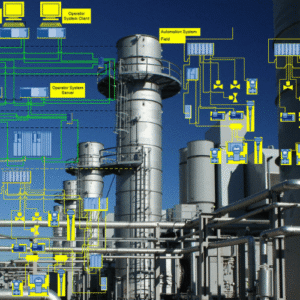
In today’s rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, industrial automation has become more than a technological upgrade—it’s a strategic necessity. As industries pursue higher efficiency, enhanced safety, and consistent product quality, automation emerges as the backbone that empowers factories to operate smarter, faster, and with greater precision.
Industrial automation integrates advanced control systems, intelligent sensors, data-driven platforms, and machine interfaces to streamline operations from end to end. It replaces repetitive manual tasks, minimizes human error, and enhances real-time decision-making. Whether in food processing, chemical plants, packaging lines, or heavy manufacturing, automation is reshaping how businesses approach productivity and sustainability.
Why Industrial Automation Matters More Than Ever
1. Higher Productivity & Faster Throughput
Automated systems ensure continuous, uninterrupted operation, enabling facilities to achieve production rates that would be impossible through manual processes. Smart controls, PLCs, and industrial HMIs synchronize every stage of the line, reducing delays and boosting output.
2. Enhanced Accuracy & Consistency
With automation, precision becomes the norm. Systems maintain exact parameters—weight, speed, temperature, torque, pressure—with minimal variation. This level of consistency ensures product uniformity and reduces waste.
3. Energy & Resource Optimization
Modern automation platforms are designed to optimize power usage, reduce material loss, and extend equipment lifespan. The result is lower operational costs and a more sustainable manufacturing footprint.
4. Improved Safety & Reduced Risk
Automated protections, interlocks, and real-time monitoring dramatically reduce workplace accidents. Workers no longer need to engage directly with hazardous equipment, while systems automatically detect and respond to unsafe conditions.
5. Better Data, Smarter Decisions
Data has become one of the most valuable assets in modern factories. Automation systems continuously collect and analyze information, enabling predictive maintenance, performance tracking, and rapid troubleshooting. This transforms decision-making from reactive to proactive.
Core Components of Industrial Automation
1. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs)
PLCs act as the “brain” of the system, controlling processes with reliability and speed. They handle everything from timing sequences to advanced logic, motion control, and integration with other devices.
2. Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs)
HMIs bridge the gap between operators and machinery, displaying critical information and allowing real-time adjustments. Modern touch-screens offer intuitive navigation, error messages, and live diagnostics.
3. Sensors and Feedback Devices
Automation relies on accurate feedback. Sensors measure weight, speed, temperature, level, flow, and pressure—feeding data into the PLC for continuous adjustments.
4. Motor Control & Drives
Variable-frequency drives (VFDs) and servo controllers regulate motor speed, torque, and motion profiles. They ensure smooth operation and energy-efficient performance across the factory floor.
5. Industrial Networking
Although we have removed reference to modern communication protocols (as per your request), industrial networks remain essential for connecting devices, sharing data, and maintaining real-time control across production lines.
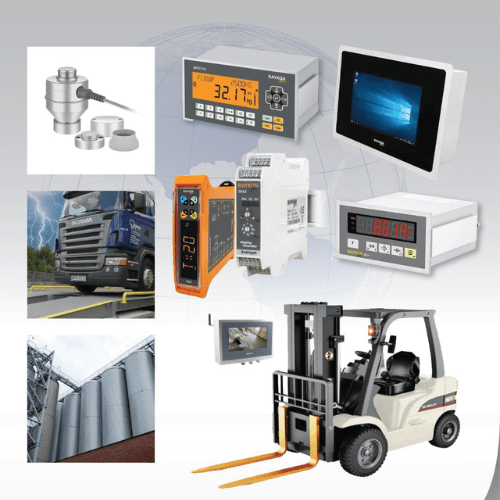
6. Weighing & Process Control
Weight indicators such as BX10, BX11, BX13, BX14, BX30, load cells, and batch controllers play a key role in industries that rely on precise dosing, filling, and measurement. These solutions provide dependable performance and seamless integration with automation systems.
Applications Across Industries
Food & Beverage
Ensuring hygienic, consistent, and fast production—filling, batching, mixing, and packaging benefit greatly from automation.
Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals
Tight control over parameters guarantees safety, accuracy, and compliance with standards.
Packaging Automation
Whether manual-assist lines or full robotic systems, automation enhances speed, reduces waste, and keeps product quality stable.
Manufacturing & Assembly
From motor controls to robot arms, automation enables high-volume, high-precision production.
Agriculture & Feed Mills
Process control systems optimize mixing, dosing, bagging, and inventory management.
How Automation Transforms Business Growth
Implementing automation is not merely an operational upgrade—it is a long-term strategic investment. Companies embracing automation gain:
-
Stronger competitiveness
-
Lower production costs
-
Higher profitability
-
Better quality assurance
-
Greater scalability for future expansion
Automation empowers businesses to meet global standards and navigate market challenges with confidence.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
As industries shift toward smarter and more connected production environments, automation will become even more essential. It is the key to achieving sustainable growth, operational excellence, and resilience in a rapidly changing world.
Whether a company is taking its first step into automation or upgrading from traditional systems, the future is clear: automation is no longer optional—it is the foundation of modern industry.