Introduction
As industries continue to evolve at an accelerated pace, Track & Trace systems have become a fundamental requirement across modern manufacturing and supply chain operations.
Today, companies are no longer focused only on productivity and quality — the ability to track every stage of a product’s lifecycle from raw material input to the final delivery has become a global standard for safety, compliance, and consumer trust.
Track & Trace provides full visibility and documentation of the product’s journey, enabling manufacturers to control processes, reduce errors, comply with international regulations, and protect their brands from counterfeiting.
What Is Track & Trace?
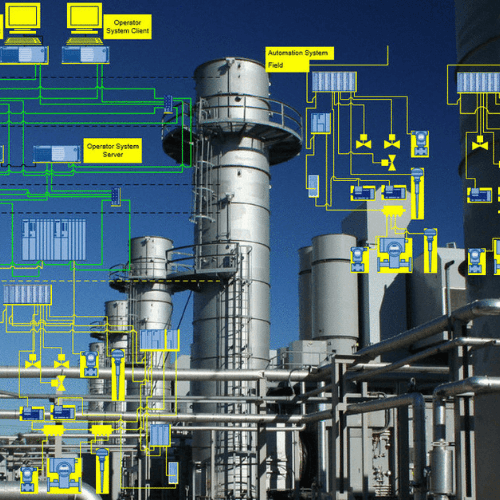
Track & Trace is an integrated system designed to identify, record, monitor, and verify a product throughout every stage of production, packaging, distribution, and delivery.
The system relies on several core components:
-
Unique Identification Codes (UID)
-
Serial Numbers
-
QR Codes / DataMatrix Codes
-
Vision Inspection Systems
-
Centralized Data Management Software
These elements work together to create a complete digital record for each product unit.
Why Track & Trace Has Become Essential
1. Anti-Counterfeiting Protection
In high-risk sectors such as pharmaceuticals, food, and electronics, a unique identification code is a critical shield against product duplication and market fraud.
2. Regulatory Compliance
Governments and international authorities now require serialization and aggregation, including:
-
GS1 Compliance
-
Serialization Standards
-
Aggregation Requirements
Track & Trace ensures manufacturers meet these regulations smoothly and accurately.
3. Full Transparency Across the Supply Chain
Every action performed on the product is logged digitally, creating a transparent and traceable product history.
4. Improved Quality Control
Real-time connection between machines, software, and databases enables fast detection and elimination of errors.
5. Efficient Product Recall
If a defect or contamination occurs, manufacturers can isolate the exact affected batch instead of recalling entire shipments — saving time, effort, and cost.
Main Components of a Track & Trace System
1. Coding Systems
Product identification begins with proper coding technologies such as:
-
Laser Marking
-
Inkjet Coding
-
Thermal Transfer Printing
These systems apply a unique and scannable code on each product or package.
2. Vision Inspection Systems
High-resolution cameras verify:
-
Code readability
-
Content accuracy
-
Print quality
-
Product integrity
These systems ensure that invalid or unreadable codes do not pass forward.
3. Central Database
The database acts as the “brain” of the system, storing:
-
Serial numbers
-
Production time
-
Batch/lot information
-
Aggregation data
-
Movement and shipment details
This provides complete traceability across all stages.
4. Aggregation Systems
Aggregation links all levels of packaging:
-
Single product → Small package
-
Package → Carton
-
Carton → Pallet
This allows seamless tracking of every product inside every package throughout the supply chain.
5. Software Platform
Track & Trace software manages:
-
Serial number generation
-
Communication with production lines
-
Integration with ERP/MES systems
-
Reporting and analytics
-
Regulatory data exchange with government portals
How Track & Trace Works in a Production Line
-
Serial numbers are generated through the software.
-
Codes are printed on each product or package.
-
Vision systems verify code correctness and print quality.
-
Data is recorded instantly in the central database.
-
Products are aggregated into cartons and pallets.
-
Shipment movement is monitored until it reaches distributors or customers.
-
Every step is documented digitally for full traceability.
Industrial Applications of Track & Trace
1. Pharmaceutical Industry
The most regulated sector globally — serialization and aggregation are mandatory.
2. Food & Beverage Industry
To ensure food safety from source to consumer.
3. Electronics Manufacturing
To track components and prevent counterfeit parts.
4. Cosmetics Industry
To maintain product authenticity and quality.
5. Engineering & Metal Industries
For tracking spare parts and manufacturing processes.
Key Benefits of Implementing Track & Trace
-
Minimizes production losses and operational waste
-
Enhances customer trust and brand protection
-
Enables accurate problem identification
-
Improves planning and production efficiency
-
Ensures full compliance with international laws
-
Supports digital transformation and Industry 4.0 initiatives
Challenges Solved by Track & Trace
-
Lost or misplaced products during manufacturing
-
Difficulty in monitoring shipments
-
Quality issues with no clear root cause
-
Manual reporting errors
-
High levels of product counterfeiting
Conclusion
Track & Trace is now one of the most essential systems enabling digital transformation in industry.
It goes far beyond product tracking — delivering full visibility, control, and data-driven decision-making across every stage of production and distribution.
With evolving global regulations and increasing market challenges, Track & Trace has become a strategic investment for any factory aiming to achieve higher safety, enhanced quality, and sustainable competitive advantage.